Google™ Search
December 25, 2025
The RBVI wishes you a safe and happy holiday season!
See our
2025 card and the
gallery of previous cards back to 1985.
September 22, 2025
Mac users may wish to defer upgrading to MacOS Tahoe.
Currently on that OS the Chimera graphics window is shifted so that it covers
the command and status lines.
March 6, 2025
Chimera production release 1.19 is now available,
fixing the ability to fetch structures from the PDB
(1.19 release notes).
Previous news...
Please note that
UCSF Chimera is legacy software that is no longer being developed or supported.
Users are strongly encouraged to try
UCSF ChimeraX, which is under active development.

UCSF Chimera is a program for the interactive visualization
and analysis of molecular structures and related data,
including density maps, trajectories, and sequence alignments.
It is available free of charge for noncommercial use.
Commercial users, please see
Chimera commercial licensing.
We encourage Chimera users to try ChimeraX
for much better performance with large structures, as well as other major
advantages
and completely new features in addition to nearly all the capabilities
of Chimera (details...).
Chimera is no longer under active development.
Chimera development was supported by a grant from the
National Institutes of Health (P41-GM103311)
that ended in 2018.
The
PipesAndPlanks
tool shows protein helices as “pipes” (cylinders)
and strands as “planks” (rectangular boxes), with connectors
for the intervening coil. Adjustable settings include pipe radius, plank
width, colors, and whether to include arrowheads to show chain
N→C directionality
(see image how-to).
(More features...)
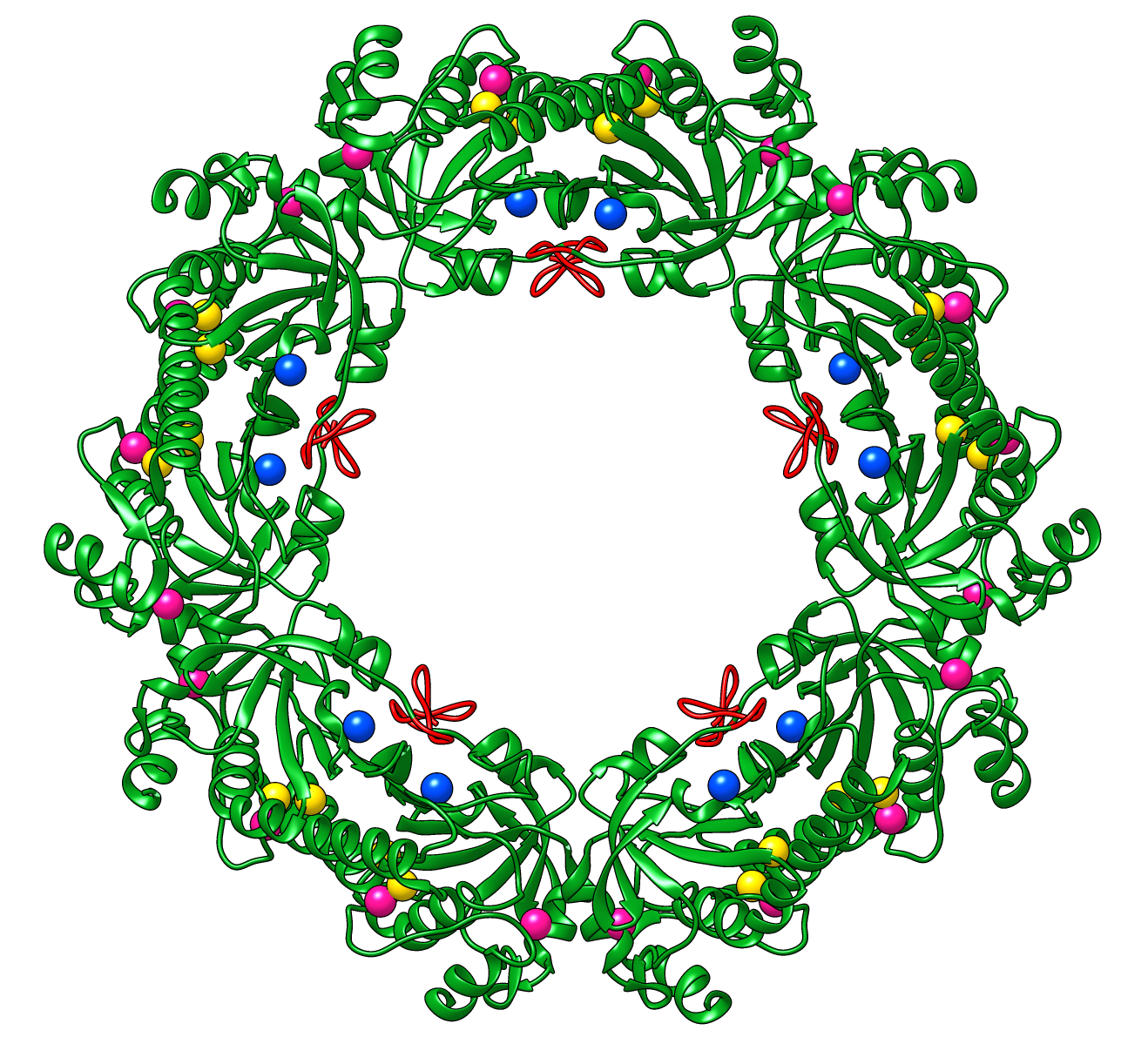

Peroxiredoxins are enzymes that help cells cope with stressors
such as high levels of reactive oxygen species. The image shows a decameric
peroxiredoxin from human red blood cells (Protein Data Bank entry
1qmv),
styled as a holiday wreath.
See also the RBVI
holiday card gallery.
(More samples...)