Structure Measurements enables measurements of molecular geometry (distances, bond angles, and torsion angles) and adjustments of torsion angles. It has three sections shown as index cards:
Only one card is shown at a time, and clicking the tab for another brings it to the front. Structure Measurements can be opened by starting any of its sections; there are several ways to start each of the three sections, classified as tools in the Structure Analysis category.Save saves measurements to a file. Close closes the measurements panel, and Help opens this manual page in a browser window.
The Distances section of the Structure Measurements panel is a table of distance monitors (measurements that update if there are changes).
There are several ways to start Distances, a tool in the Structure Analysis category. Distance monitors can be created in three ways:
| Distances Panel - simple atom listings |
|---|
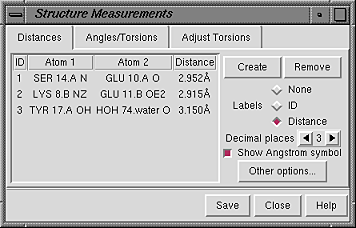 |
The simple atom listing consists of residue name, residue specifier (number.chain), and atom name; the alternative is an atom specification string (see the Adjust Torsions figure). Atomspec display style in the General preferences controls which style is used.
Clicking on a distance listing allows it to be deleted with the Remove button. If there is only one distance monitor, it is not necessary to click on its listing before using Remove. Clicking on a distance listing selects the corresponding distance monitor pseudobond and deselects any others; if the distance monitor is already selected, it is deselected.
The Labels setting applies to all distance monitors and can be switched among:
Lines representing distance monitors are pseudobonds in a group named distance monitor. Clicking Other options... brings up a panel of pseudobond attributes for this group, allowing changes in various aspects of their appearance such as color, linewidth, and whether the lines are dashed. When an individual pseudobond is selected, its attributes can be altered with the Selection Inspector.
The Angles/Torsions section of the Structure Measurements panel is a table of angle monitors (measurements that update if there are changes). A "bond angle" is measured for three atoms and a "torsion angle" for four atoms; however, it is not necessary for the atoms to be contiguous or even bonded to one another. Angles/Torsions reports changes but cannot be used to change the angles. To modify torsions, use Adjust Torsions instead.
There are several ways to start Angles/Torsions, a tool in the Structure Analysis category. Angle monitors can be created in various ways:
The Decimal places setting controls the appearance of the angle values; the number of digits shown after the decimal can be changed by clicking or holding down one of the arrows on either side of the value. Atoms can be listed with a simple style consisting of residue name, residue specifier (number.chain), and atom name (see the Distances figure) or with an atom specification string (see the Adjust Torsions figure). Atomspec display style in the General preferences controls which style is used.
The command angle can also be used to measure bond angles and torsions; however, it yields a static measurement rather than a continuously updating monitor.
The Adjust Torsions section of the Structure Measurements panel is a table of active (rotatable) torsions.
There are several ways to start Adjust Torsions, a tool in the Structure Editing category. Torsions can be activated in several different ways:
| Adjust Torsions Panel - atom specification listings |
|---|
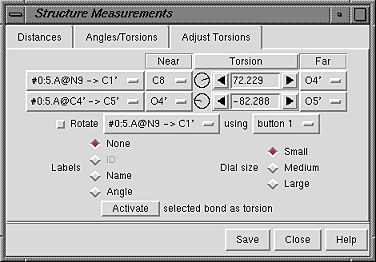 |
If the four atoms defining a torsion are called 1-2-3-4, 1 is the Near atom and 4 is the Far atom, which will move when the bond is rotated. The angle in degrees as defined by the current Near and Far atoms is shown in the Torsion column. Torsion can be toggled to Delta; the reported value is then the angle in degrees relative to the starting angle, and there are no Near and Far columns.
 A bond can be rotated by entering a new angle value (and pressing return),
clicking the arrows flanking the angle value,
or manipulating the dial. The Dial size can be set to
Small, Medium, or Large. Further, torsions
can be manipulated in the graphics window with the mouse.
This can be done by checking
Rotate [torsion] using [button]
and choosing the desired torsion and mouse button from the pulldown menus.
A bond can be rotated by entering a new angle value (and pressing return),
clicking the arrows flanking the angle value,
or manipulating the dial. The Dial size can be set to
Small, Medium, or Large. Further, torsions
can be manipulated in the graphics window with the mouse.
This can be done by checking
Rotate [torsion] using [button]
and choosing the desired torsion and mouse button from the pulldown menus.
The column with atoms 2->3 contains a pulldown menu for each active rotation:
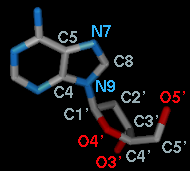
When atom 2 is bonded to more than two atoms, there is more than one possible Near atom, and alternatives (if any) are available in a pulldown menu from the current Near atom name. Likewise, when atom 3 is bonded to more than two atoms, there is more than one possible Far atom, and alternatives (if any) are available in a pulldown menu from the current Far atom name. For the first torsion in the example (figures above), there are two choices for the Near atom, C8 and C4, and two choices for the Far atom, O4' and C2'. For the second torsion, there are two choices for the Near atom, O4' and C3', and only one possible Far atom, O5'. Of course, if Reverse is used, the Near and Far choices are interchanged, and in the Delta mode, there are no Near and Far columns.
The Labels setting applies to all active torsions and can be switched among: